What Is A Mac Address Used For
A MAC (Media Access Control) address, sometimes referred to as a hardware address or physical address, is an ID code that's assigned to a network adapter or any device with built-in networking capability, such as a printer. While an IP address can potentially be assigned to any device, a MAC address is 'burned into' a given device from the factory. Follow the steps for the operating system that you use. Example of a MAC address: 00:00:00:a1:2b:cc. Every device connected to your home network has a unique MAC address. If your computer has multiple network adapters (for example, an Ethernet adapter and a wireless adapter), each adapter has its own MAC address.
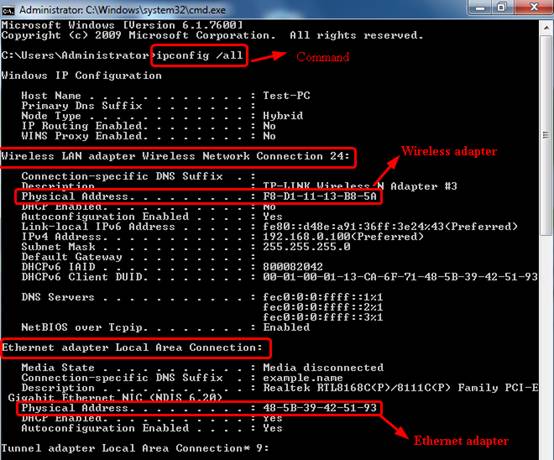
We can find mac address (physical address) of a computer using the command ‘getmac‘. This can be used to get mac address for remote computers also. Below are few examples on how to use this command. It works on XP, Vista, Windows 7, Server 2003 and Server 2008 operating systems. Get mac addresses from CMD.
A broadcast address is a network address at which all devices connected to a multiple-access communications network are enabled to receive datagrams. A message sent to a broadcast address may be received by all network-attached hosts.
Uninstall CAC enabling programs: ActivClient for Mac, CSSi, Centrify Express, PKard, CACKey, and / or OpenSC. Use DTS on your Mac. Watch Mac Videos (Including setting up CACKey with Firefox) Update the firmware on an SCR331 using TENS. Downgrade the firmware on the IOGear GSR202, 202V, and 203 CAC Readers. Other Information. ActivClient enables usage of PKI certificates and keys, one-time passwords and static passwords on a smart card or USB token to secure desktop applications, network login, remote access, web login, e-mail and electronic transactions. Activclient for mac.
Experience the world's most realistic and professional digital art & painting software for Mac and Windows, featuring hundreds of realistic brushes, paint and tutorials. Painter 2020 sets the standard for professional digital art. With a streamlined workflow, all-new brushes, enhanced color selection and more, see how Painter allows artists to. Paint by number software for mac. Apple’s OS X 10.10 Yosemite software introduced so many new features that users will still be trying to learn them several months after installing the update. There’s a hidden paint.
In contrast, a multicast address is used to address a specific group of devices and a unicast address is used to address a single device.
For network layer communications, a broadcast address may be an IP address. In Ethernet networks, it can be a MAC address.
IP networking[edit]
In Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) networks, broadcast addresses are special values in the host-identification part of an IP address.[1] The all-ones value was established as the standard broadcast address for networks that support broadcast.[1] Bootable usb for mac on windows. This method of using the all-ones address was first proposed by R. Gurwitz and R. Hinden in 1982.[2] The later introduction of subnets and Classless Inter-Domain Routing changed this slightly, so that the all-ones host address of each subnet is that subnet's broadcast address.[3][4]
As shown in the example in the table below, the broadcast address for an IPv4 host can be obtained by taking the bit complement (bitwise NOT) of the subnet mask and then performing a bitwise OR operation with the host's IP address. In short, take the host's IP address and set to '1' any bit positions which hold a '0' in the subnet mask. For example, for broadcasting a packet to an entire IPv4 subnet using the private IP address space 172.16.0.0/12, which has the subnet mask 255.240.0.0 (again, refer to the table below to see how this is obtained), the broadcast address is 172.16.0.0 bitwise ORed with 0.15.255.255 = 172.31.255.255. Sticker for macbook pro 15.
| Network IP address breakdown for 172.16.0.0/12 | Binary form | Dot-decimal notation |
|---|---|---|
| In bold below is shown the host part (suffix) of the IP address, with the network address prefix being the non-bold bits to its left. To obtain the broadcast address, the host bits get set to all 1's, while the network address prefix bits remain intact. | ||
| 1. Network IP Address | 10101100.00010000.00000000.00000000 | 172.16.0.0 |
2. Subnet Mask, or just 'Netmask' for short (The '/12' in the IP address in this case means only the left-most 12 bits are 1s, as shown here. This reserves the left 12 bits for the network address (prefix) and the right 32 - 12 = 20 bits for the host address (suffix).) | 11111111.11110000.00000000.00000000 | 255.240.0.0 |
| 3. Bit Complement (Bitwise NOT) of the Subnet Mask | 00000000.00001111.11111111.11111111 | 0.15.255.255 |
| 4. Broadcast address (Bitwise OR of 1. Network IP Address and 3. Bit Complement of the Subnet Mask. This makes the broadcast address the largest possible IP address (and host address, since the host address portion is all 1s) for any given network address.) | 10101100.00011111.11111111.11111111 | 172.31.255.255 |
A special definition exists for the IP address 255.255.255.255. It is the broadcast address of the zero network or 0.0.0.0, which in Internet Protocol standards stands for this network, i.e. the local network. Transmission to this address is limited by definition, in that it is never forwarded by the routers connecting the local network to other networks.
IP broadcasts are used by BOOTP and DHCP clients to find and send requests to their respective servers.
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) does not implement this method of broadcast, and therefore does not define broadcast addresses. Instead, IPv6 uses multicast addressing to the all-hosts multicast group. No IPv6 protocols are defined to use the all-hosts address, though; instead, they send and receive on particular link-local multicast addresses. This results in higher efficiency, because network hosts can filter traffic based on multicast address and do not need to process all broadcasts or all-hosts multicasts.
Ethernet[edit]
Broadcast is possible also on the underlying data link layer in Ethernet networks. Frames are addressed to reach every computer on a given LAN segment if they are addressed to MAC addressFF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. Ethernet frames that contain IP broadcast packages are usually sent to this address.
Ethernet broadcasts are used by Address Resolution Protocol and Neighbor Discovery Protocol to translate IP addresses to MAC addresses.
IPX networking[edit]
Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) allows broadcast. A packet with network number of FFFFFFFF is sent to all networks available. When the node number is specified as FFFFFFFFFFFF, the packet is intended to be received by all hosts in the network.
AppleTalk[edit]
The AppleTalk protocol allows broadcast. When the node ID is specified as 255, a packet is sent to all networks available.
See also[edit]
- UDP Helper Address — a tool for routing DHCP and BOOTP broadcast requests across subnet boundaries
What Is A Mac Number
References[edit]
What Is An Ip Address
- ^ abJ. Mogul (October 1984). BROADCASTING INTERNET DATAGRAMS. doi:10.17487/RFC0919. RFC 919.
- ^IEN 212, IP - Local Area Network Addressing Issues, Robert Gurwitz, Robert Hinden, Bolt Beranek and Newman (BBN) (September 1982)
- ^J. Mogul (October 1984). BROADCASTING INTERNET DATAGRAMS IN THE PRESENCE OF SUBNETS. doi:10.17487/RFC0922. RFC 922.
- ^RFC922, Broadcasting Internet Datagrams In the Presence of Subnets, J. Mogul (October 1984)